Herbicides containing tribenuron-methyl provide effective control of dicotyledonous weeds in sunflower crops due to their systemic action.
Within a few hours after treatment, the product penetrates the weeds, stopping their growth and development. Visible signs of herbicidal action appear in 5-8 days, and complete weed death occurs within 2-3 weeks.
It is important that the herbicide acts only on those weeds that have already sprouted at the time of application.
Benefits of using tribenuron-methyl:
- Destruction of annual dicotyledonous weeds that are inaccessible to traditional soil herbicides
- The only reliable method of thistle control after sunflower emergence
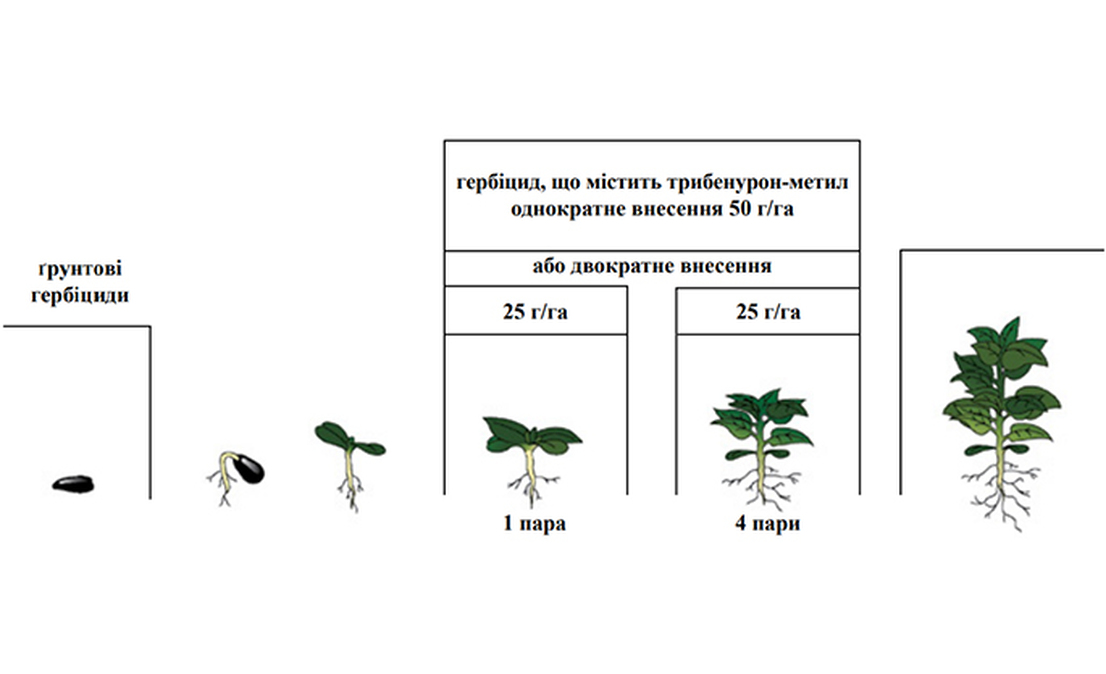
- Flexibility of application from 1 to 4 pairs of true sunflower leaves
- Possibility to adjust herbicide consumption rates or apply it in two stages depending on field conditions.
- No restrictions for the following crops in the crop rotation
The line of SU-hybrids of sunflower of VNIS selection is represented by hybrids: Mastak, Mahnum, Sonyachniy nastriy, Vehas, Folk, Amato, Almera, Shenon. These hybrids have genetic resistance to tribenuron-methyl at a rate of 50 g/ha, which makes them the best choice for this technology.
SU-hybrids technology involves sowing specialized sunflower hybrids and applying herbicide after the emergence of cultivated plants. With SU, your crops will always be under reliable protection!
Partial yellowing of sunflower plants and/or temporary growth retardation (up to 5 days) after application is a physiological reaction of hybrids to the product. Usually, normal plant growth is restored within 5 days.
However, an increase in the single rate (higher than recommended) of the drug consumption can lead to deformation or absence of the main basket and the formation of unproductive additional baskets in the leaf axils instead.
Developmental stage of cultivated plants
The treatment is applied in the period from 1 to 4 pairs of true leaves in sunflower plants once or in two stages of half the dose during the specified period.
Weed growth stage
The effectiveness of the herbicide application depends on the stage of weed development at the time of application. Maximum effectiveness will be observed when weed plants are at the following stages of development:
- ragweed - up to 2 true leaves at most;
- white quinoa - up to 4 true leaves at most;
- tenacious crabgrass - up to the stage of 3-4 rings:
- other annual dicots - up to 4-6 true leaves;
- perennial dicotyledons (thistles) - rosette stage - beginning of stem growth.
Factors affecting the level of resistance of sunflower hybrids to tribenuron-methyl-based herbicides
The resistance of sunflower hybrids to the herbicide is determined by their specific genetics. However, there are a number of factors that can significantly affect the level of resistance of a hybrid during the period of herbicide application. These are factors of natural origin and factors of chemical nature.
Natural factors:
- dry weather conditions;
- conditions of excessive moisture;
- low (less than +12°C) or high (more than +25°C) air temperatures during the application period;
- sharp fluctuations in night and day temperatures during the period of herbicide application
Chemical factors:
- negative effect of other herbicides, if their application is close in time to the application of the preparation containing tribenuron-methyl
- insecticides from the group of organophosphorus compounds;
- fertilizers applied by spraying during the period of application of the preparation.
The warnings in the technology of using herbicides containing tribenuron-methyl are aimed at preventing toxicity of sunflower plants:
- in case of necessity to apply anti-cereal herbicides, the interval between the application of such preparations and the herbicide should be at least 7 days;
- it is not recommended to use insecticides from the group of organophosphorus compounds;
- it is forbidden to fertilize vegetative sunflower plants by spraying simultaneously (in tank mixtures) with the application of the herbicide, as the herbicide's entry into the plants is accelerated, which can cause their toxicity.
Control of sunflower leafhoppers resistant to tribenuron-methyl herbicide
Sunflower borer is resistant to inhibitor herbicides (sulfonylurea derivatives, imidazolinones, triazole pyrimidines). To destroy the carrion of such sunflower when growing the next crop of the crop rotation, it is mandatory to use drugs with a different mechanism of action, for example, growth and development regulators (products containing 2,4-D, dicamba, fluroxypyr, clopiramide, MCPA).
Request a free consultation by phone: 0 800 302 032 (calls are free in Ukraine) or contact your regional manager on the Sales Representatives page. Choose your own. Quality.

 Choose a country
Choose a country