The basis for successful sunflower nutrition
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for sunflower. They all have different but equally important effects on the crop.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen (N) is the main building block for all crops and sunflower is no exception. Thanks to this element, green mass, root system, and generative organs grow. Nitrogen is an element of protein, a component of enzymes, hormones, and chlorophyll.

Thus, with a lack of nitrogen in the plant, growth inhibition, premature yellowing, cotyledons drying out - at the beginning of the growing season and early death of the lower leaves starting from the tip, yellowing of veins, chlorosis - at the later stages of ontogeny are observed. In this case, the yield shortfall and low oil content are expected.


However, given the high nitrogen demand of plants, it should not be overused. Excessive doses of fertilizers can lead to the development of diseases (phomopsis, white rot), lodging of crops due to excessive growth of the ground part, an increase in the growing season and an increase in protein content and, as a result, a decrease in oil content.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus (P) is also a component of chlorophyll, DNA, and cell membranes, and plays an important role in the energy and growth process. It promotes the absorption of nitrogen, affects faster early maturity, and has a huge impact on the root system, starting with seed germination and its growth into deeper layers to absorb deficient moisture, which is invaluable for southern Ukraine. It is worth noting that phosphorus is an indispensable material for building the generative part and contributes to high oil content.

Lack of phosphorus inhibits plant growth and development, and the root system develops poorly. Symptoms of deficiency appear primarily on old leaves. The color of the leaves changes from dark green to a bluish-lilac hue, brownish-red spots appear, and later, their core dries up and dies. Yellow-brown, brown and black-brown color may appear along the edges of the leaves. There is a slowdown in the developmental phases, followed by flowering and ripening.
Phosphorus is a slow-moving element in the soil, so it quickly reacts with other elements, forms new compounds and becomes inaccessible, which is why the plant absorbs about 15-22%.
Potassium (K)
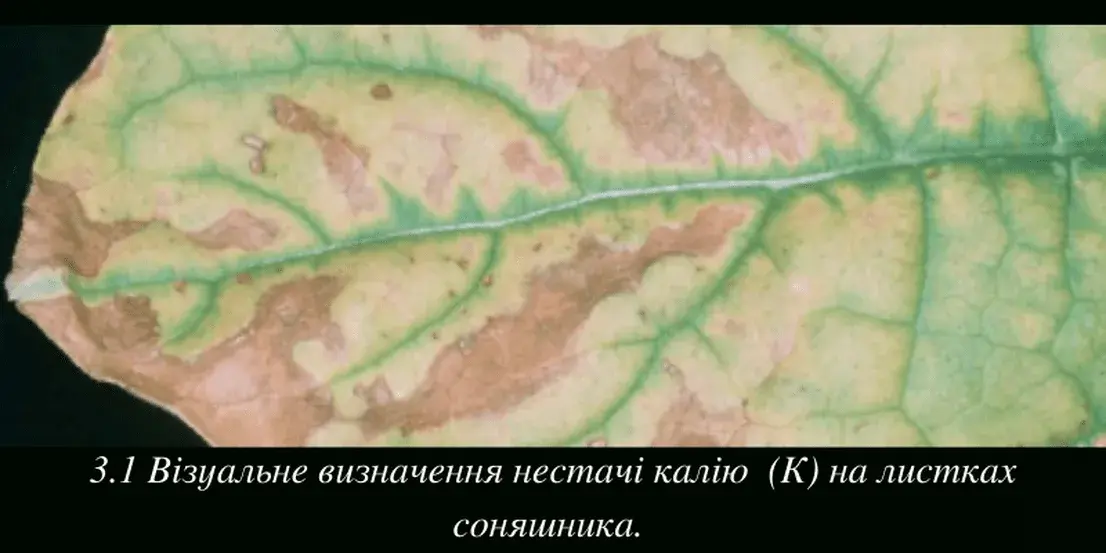
And finally, potassium (K). Without it, we will not get a high yield. After all, it is responsible for turgor, the efficient use of moisture from the soil, which means that this element plays an important role in the plant's drought resistance. It is involved in the formation of protein and starch, moves nutrients and water through the plant, which directly affects the ripening of sunflower. In general, it has a positive effect on the plant's immunity, resistance to fungal diseases, drought and other stress factors. It improves the final quality of products.
Its deficiency can be seen in fields that are very poor in this element. As a rule, this is the Forest-Steppe and Polissya zones, where the need for potassium fertilization is undeniable. As for the Steppe zone, we need to pay attention to the content of potassium in the available form. You should not underestimate its effect on sunflower. If you see that the leaves have become more rustling, curled from the sides, as well as yellowing of the lower leaves and their death, this is a deficiency of potassium, which leads to a brittle, thin stem and, as a result, a decrease in oil content and the amount of saturated and unsaturated acids.
Speaking about the critical phases of sunflower, when the plant has the greatest need for nutrients, it should be noted that they are absorbed unevenly. The largest amount of nitrogen is absorbed in the phase of basket ovary to the end of flowering, potassium - from basket formation to ripening, phosphorus - the phase of germination-flowering.
For the formation of 1 ton of crop, the plant needs nitrogen (N) -40 kg, phosphorus (P) - 30 kg, potassium (K) - 120 kg.
Other factors should also be taken into account when forming a mineral nutrition system:
- return of organic mass from the by-products of the predecessor;
- moisture supply is the main limiting factor;
- soil type along with the results of its analysis on the presence and availability of elements in it.
Recommended fertilizer application rate
Typically, 60-90 kg is the optimal dose of nitrogen fertilizers in the active ingredient, 40-70 kg of phosphorus fertilizers, and 150-200 kg of potash fertilizers (provided that potassium is not available in an accessible form).
It is worth noting that phosphorus is found in the plant in the stem and in the lower part of the basket. During filling, phosphorus moves to the seeds and continues to be absorbed by the root system. Thus, about 75% of phosphorus is removed from the field. As for potassium, we have the opposite picture. It remains with plant residues on the field, localized in the stems and the basket.
The need for potassium and phosphorus can be satisfied by complex fertilizers for the main cultivation (diammophoska, nitroammophoska, potassium chloride, ammophos, nitroammophos, double superphosphate, etc.) Nitrogen demand - pre-sowing application of nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, urea, calcium nitrate, ammonium sulfate)
Organic fertilizers are best applied under the preceding crop in the amount of 20 t/ha of manure in the fall for plowing. The application of liquid manure will worsen the soil structure, to which sunflower is sensitive.
A more accurate fertilizer application rate is best agreed with a qualified agronomist, taking into account the presence of mobile forms of elements based on the results of diagnostics.

 Choose a country
Choose a country